Mybatis 代码流程浅析
Mybatis 代码流程浅析
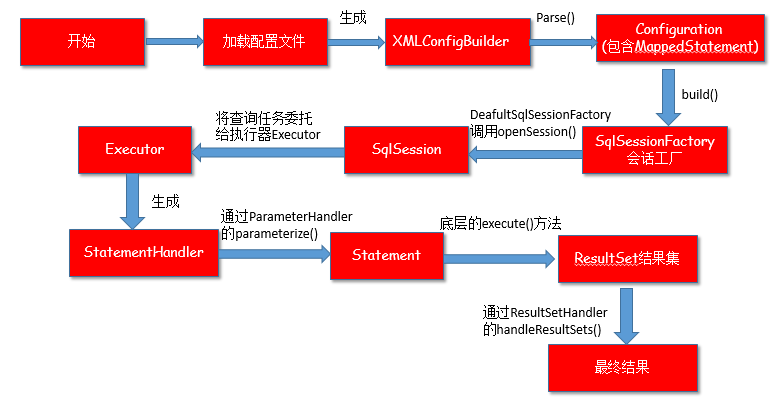
加载配置文件
典型的 MyBatis 全局配置文件如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<!-- 和spring整合后 environments配置将废除 -->
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<!-- 使用jdbc事务管理 -->
<transactionManager type="JDBC" />
<!-- 数据库连接池 -->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="url"
value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?characterEncoding=utf-8" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="123456" />
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="sqlMapper/userMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
创建一个 sqlSessionFactory
Mybatis 首先会解析 XML 文件生成 Configuration:
public Configuration parse() {
if (parsed) {
throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
}
parsed = true;
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
return configuration;
}
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties")); //issue #117 read properties first
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
settingsElement(root.evalNode("settings"));
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments")); // read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
其中核心的是对于 Mapper 的解析,mapperElemet()方法是解析 mapper 映射文件的,具体代码如下:
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage);
} else {
String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource");
String url = child.getStringAttribute("url");
String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class");
if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) {//进入该判断
ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(url);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url);
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, url, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url == null && mapperClass != null) {
Class<?> mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass);
configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface);
} else {
throw new BuilderException("A mapper element may only specify a url, resource or class, but not more than one.");
}
}
}
}
}
根据以上代码可以分析,在写 mapper 映射文件的地址时不仅可以写成 resource,还可以写成 url 和 mapperClass 的形式,由于我们用的是 resource,所以直接进入第一个判断,最后解析 mapper 映射文件的方法是:
private void configurationElement(XNode context) {
try {
String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");
if (namespace.equals("")) {
throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");
}
builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);
cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref"));
cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));
parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap"));
resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));
sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing Mapper XML. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
其中具体解析每一个 sql 语句节点的是
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));
进入这个方法一层层深究,最后到这里可以知道 MappedStatement 是由 builderAssistant(即 MapperBuildAssistant)创建的。
public void parseStatementNode() {
...
builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType,
fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap, parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass,
resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered,
keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, resultSets);
}
最后进入方法 addMappedStatement(),mappedStatement 最后以 id 为键保存在了 Configuration 中的一个 map 变量 mappedStatements 中。
public MappedStatement addMappedStatement(
String id,
SqlSource sqlSource,
StatementType statementType,
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType,
Integer fetchSize,
Integer timeout,
String parameterMap,
Class<?> parameterType,
String resultMap,
Class<?> resultType,
ResultSetType resultSetType,
boolean flushCache,
boolean useCache,
boolean resultOrdered,
KeyGenerator keyGenerator,
String keyProperty,
String keyColumn,
String databaseId,
LanguageDriver lang,
String resultSets) {
if (unresolvedCacheRef) throw new IncompleteElementException("Cache-ref not yet resolved");
id = applyCurrentNamespace(id, false);
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
MappedStatement.Builder statementBuilder = new MappedStatement.Builder(configuration, id, sqlSource, sqlCommandType);
statementBuilder.resource(resource);
statementBuilder.fetchSize(fetchSize);
statementBuilder.statementType(statementType);
statementBuilder.keyGenerator(keyGenerator);
statementBuilder.keyProperty(keyProperty);
statementBuilder.keyColumn(keyColumn);
statementBuilder.databaseId(databaseId);
statementBuilder.lang(lang);
statementBuilder.resultOrdered(resultOrdered);
statementBuilder.resulSets(resultSets);
setStatementTimeout(timeout, statementBuilder);
setStatementParameterMap(parameterMap, parameterType, statementBuilder);
setStatementResultMap(resultMap, resultType, resultSetType, statementBuilder);
setStatementCache(isSelect, flushCache, useCache, currentCache, statementBuilder);
MappedStatement statement = statementBuilder.build();
configuration.addMappedStatement(statement);
return statement;
}
最后回到我们的创建 sqlSessionFactory 上,之前的一切都是为了生成一个 sqlSessionFactory 服务的
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}
从上面的代码可以看出最后是通过以 Configuration 为参数 build()方法生成 DefautSqlSessionFactory。
创建 sqlSession
public SqlSession openSession() {
return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false);
}
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
// 返回一个 SqlSession,默认使用 DefaultSqlSession
public DefaultSqlSession(Configuration configuration, Executor executor, boolean autoCommit) {
this.configuration = configuration;
this.executor = executor;
this.dirty = false;
this.autoCommit = autoCommit;
}
executor 在这一步得到创建,具体的使用在下一步。
执行具体的 sql 请求
- 根据具体传入的参数,动态地生成需要执行的 SQL 语句,用 BoundSql 对象表示
- 为当前的查询创建一个缓存 Key
- 缓存中没有值,直接从数据库中读取数据
- 执行查询,返回 List 结果,然后 将查询的结果放入缓存之中
- 根据既有的参数,创建 StatementHandler 对象来执行查询操作
- 将创建 Statement 传递给 StatementHandler 对象,调用 parameterize()方法赋值
- 调用 StatementHandler.query()方法,返回 List 结果集
在我的代码里执行的是
User user = sqlSession.selectOne("test.findUserById", 1);
具体到里面的方法就是
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
//1.根据Statement Id,在mybatis 配置对象Configuration中查找和配置文件相对应的MappedStatement
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
//2. 将查询任务委托给MyBatis 的执行器 Executor
List<E> result = executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
return result;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
在这里通过 statementId 拿到了我们在第一步存在 map 里面的 MappedStatement。SqlSession 根据 Statement ID, 在 mybatis 配置对象 Configuration 中获取到对应的 MappedStatement 对象,然后调用 mybatis 执行器来执行具体的操作。再继续看 query()和 queryFromDatabase() 这两个方法:
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
queryStack++;
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
deferredLoads.clear(); // issue #601
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
clearLocalCache(); // issue #482
}
}
return list;
}
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
List<E> list;
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
localCache.putObject(key, list);
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
}
return list;
}
在这两个方法里面会为当前的查询创建一个缓存 key,如果缓存中没有值,直接从数据库中读取,执行查询后将得到的 list 结果放入缓存之中。紧接着看 doQuery()在 SimpleExecutor 类中重写的方法
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
return handler.<E>query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
Statement 连接对象就是在这里创建的,因此 Executor 的作用之一就是创建 Statement 了,创建完后又把 Statement 丢给 StatementHandler 返回 List 查询结果。接下来再看一下这里的两个方法 prepareStatement()和 query()的具体实现
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
stmt = handler.prepare(connection);
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}
public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement;
ps.execute();
return resultSetHandler.<E> handleResultSets(ps);
}
prepareStatement()是创建 Statement 的具体实现方法,调用 parameterize()对创建的 Statement 对象设置参数,即为我们设为占位符的地方赋上指定的参数,parameterize()方法再深入进去就是调用 ParameterHandler 的 setParameters()方法具体赋值了。这里的 query()是调用了 ResultSetHandler 的 handleResultSets(Statement) 方法。作用就是把 ResultSet 结果集对象转换成 List 类型的集合。
